How is Blockchain improving Healthcare
When talking about blockchain, the first thing that comes to our mind is most probably cryptocurrencies and, especially Bitcoin. Most people are expecting that the next few years will bring big, disrupting changes in everything related with economy and finances. Surprisingly enough, a survey conducted by the IBM Institute for Business Value in 2017 showed that healthcare executives are beginning to implant blockchains at a faster pace than banks and financial companies.
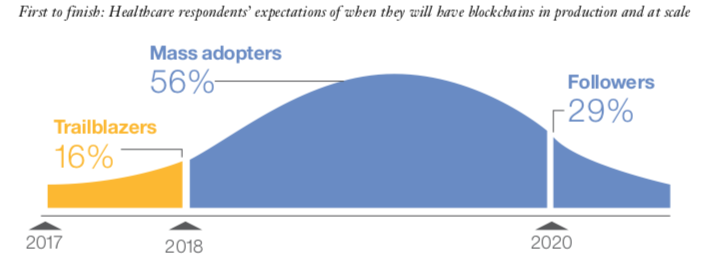
According to this study –"Healthcare rallies for blockchains", a survey conducted among 200 healthcare executives in 16 countries–, healthcare executives are not only experimenting with blockchain, they are using it. In fact, 16% of the surveyed executives expected to have a blockchain-based system up and running already in 2017, while another 56% set the deadline to 2020.
Implanting blockchain in healthcare systems will help to reduce several issues. According to the IBM survey, 66% of the executives that are first implanting blockchain-based systems expect to reduce problems due to imperfect information and 63% those due to inaccessible information. Also, 66% of them trust that blockchain will contribute to diminishing the risk of security breaches.
Medical records and Clinical trials
With our current, traditional systems, the medical/health records of any person are fragmented, in the best scenario, or most probably incomplete. During their lifetime, persons go to different hospitals, consult several physicians, take different treatments, medicines, etc… Nowadays, health data are digitalized but not yet shared. Wouldn't it be amazing to keep all this medical data together, up-to-date, and accessible from anywhere, at any time, without compromising their integrity and security? –That's exactly what a blockchain-based system can do.
Two words define blockchain better than any other: decentralization and security. While current medical records are fragmented in the intranets of different hospitals and physicians –probably in different cities or even countries– a decentralized blockchain-based system would assure that your medical history can be consulted from anywhere and by anyone who needs it. Also, new analysis, diagnosis or treatments can be added to your history from anywhere. Of course, two questions arise here: who will keep my records? And, who'll be able to access them? The answer to the first question is that no one will keep your history, your data will not exist in a physical server located somewhere, but in a decentralized network composed of thousands of computers. There will be a key to access your data though –and that's the answer to the second question: you will own the key, and only the persons you grant access to will be able to see your history and add new data – which allow privacy to be maintained by agreement about which parties can view what.
All the previous can be applied also to the records of clinical trials, especially to double-blind studies, where privacy and security breaches can compromise the results.
Regulatory compliance, billing, and claims
Another feature that blockchain may make possible is smart contracts. A smart contract is a set of rules established by two or more parts, that none of them can alter and that trigger certain actions when the given conditions are satisfied. The most common example are bids: let’s say that we create a smart contract saying that A will pay to B a certain amount of money if his team wins the next match, and the other way round, B will pay to A if B’s team is the winner. Once we’ve recorded the smart contract in a blockchain, neither A or B will be able to modify the condition. Also, when the match finishes, the smart contract itself will automatically take the money from the loser’s account and transfer it to the winner.
So, the use of this kind of contracts is not only about tracking regulatory compliance, but it can actually enforce the compliance of any rules and conditions that we can put into the contract. It’s also evident how smart contracts can improve and reduce costs of billing systems and diminish the number of claims, that nowadays are pretty frequent and costly, especially in private health care systems that run on the basis and conditions of insurance companies.
Other applications
Of course, these are just a few of the countless ways in which Healthcare industries can apply blockchains. Let’s think, for example, in how useful could be using blockchains to schedule treatments, manage medicine supplies, record data from medical devices or even control and manage contracts of employees and providers.
Nevertheless, most of the healthcare executives surveyed by IBM –even the ones that are already implementing it– don’t see the blockchain-based system as a disruption to their sector, but rather as a big and necessary improvement. How disruptive will it be, we’ll know it in the next few years.